| Affinity Tags – Streamlining the Process of Protein Purification |
| Affinity tags refer to unique peptides/proteins conjugated to recombinant proteins, facilitating efficient protein expression and purification. By fusing an affinity tag with a protein of interest, the tagged protein can be successfully isolated and purified from the cell lysate via interactions with the affinity matrix[1][2]. |
| Affinity tags include epitope tags and proteins tags. Epitope tags, such as Flag tag and His tag, can be used to localise and purify recombinant proteins. Protein tags, such as maltose binding protein (MBP) and glutathione-S-transferase (GST), can enhance protein solubility. However, it is essential to remove protein tags before structural and functional studies due to their larger size[1]. |
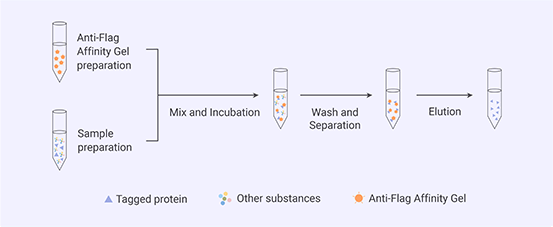 |
| Figure 1. Protein purification procedure with anti-flag affinity gel (only for reference). |
| MedChemExpress Products |
| MedChemExpress offers high-quality products for protein affinity purification. |
|
| Category |
Product Name |
Description |
| Affinity Tags |
Flag Peptide |
A tag peptide used for competitive
elution of Flag-tagged proteins from
anti-Flag resins. |
| 3X Flag Peptide |
A tag peptide with a 3-time repeated
DYKXXD motif was used for competitive
elution of Flag-tagged proteins from
anti-FLAG resins. |
| HA Peptide |
A tag peptide derived from human
influenza hemagglutinin (HA) can be used in
immunoblotting and competitive elution of
HA-tagged proteins. |
| 6X His Tag |
A tag peptide used in affinity purification of
His-tagged proteins. |
Magnetic Beads
and Affinity Gels |
Anti-Flag Magnetic Beads |
Beads are used for IP, Co-IP, and
purification of specific Flag-tagged proteins. |
| Anti-HA Magnetic Beads |
Beads are used for IP, Co-IP, and
purification of specific HA-tagged proteins. |
| Anti-His Magnetic Beads |
Beads are used for IP, Co-IP, and
purification of specific His-tagged proteins. |
| Anti-Flag Affinity Gel |
An affinity gel is used for IP and purification
of specific Flag-tagged proteins. |
|
References:  |
[1] Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(8):821-830.
[2] Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Mar-Apr;32(2):366-81. |
|

|