|
| Tumor Immunotherapy |
During tumor development, immunotherapy inhibits highly expressed
immune checkpoint molecules
to restore T-cell recognition, thereby clearing or slowing tumor progression[1]. |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitory Antibody |
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)
is the T-cell immune checkpoint molecule of greatest interest. PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitory antibodies upregulate T-cell activation and activate endogenous anti-tumor immune responses, thus exerting therapeutic effects on tumors[2]. |
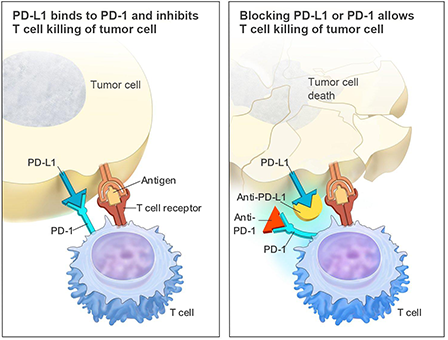 |
Figure 1. The binding of PD-L1 to PD-1 prevents T cells from killing tumor cells in the body (left panel).
Immune checkpoint inhibitory antibodies (anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-1) block the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1,
allowing T cells to kill tumor cells (right panel)[1]. |
|
|
| MedChemExpress Products |
|
|
MCE Inhibitory Antibodies are research-grade biosimilar control antibodies with the same active biological components as the original therapeutic antibody.
Target proteins include PD-1, PD-L1, CD20, HER2, EGFR, VEGFR, TNF-α, etc., which are widely used in cancer, immunity, infection and other popular research fields. |
|
Reference: |
[1] Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Mar;18(3):175-196.
[2] Immunity. 2018 Mar 20;48(3):434-452. |
 |

|