14 Feb MCE | Breakthrough Peptides in Alzheimer’s Disease

| Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is one of the most common forms of neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive cognitive decline. The pathogenesis of AD is complex and remains elusive. The disease is marked by progressive deposition and accumulation of extracellular β-amyloid (Aβ), and aggregation of intracellular Tau proteins in the brain, leading to neuronal death and cognitive impairment. However, the amyloid cascade hypothesis is widely acknowledged, especially following the recent approval of anti-amyloid antibodies for AD treatment. |
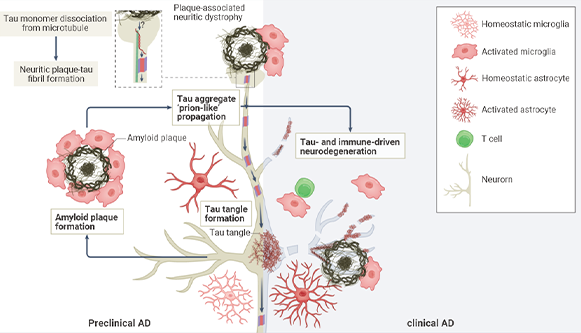
Figure 1. Mechanisms of Aβ deposition and Tau protein aggregation
leading to neurologic dysfunction and degeneration in AD[1].
• Extracellular Aβ Plaque Deposition
Aβ peptides, the main component of senile plaques found in AD patients, are derived from amyloid precursor protein (APP) through sequential cleavage by β- and γ- secretases. The resulting extracellular Aβ peptides with varying lengths (37-43 amino acids), the longer Aβ peptides (such as Aβ42) being more prone to deposit into insoluble amyloid fibrils, further deposit and accumulate, ultimately lead to neuronal death and progression of AD.
• Intracellular Tau Protein Aggregation
Tau protein, a microtubule-associated protein (MAP), normally promotes axon and dendrite growth as well as axonal transport through microtubule stabilization. In AD brains, abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation and its posttranslational modifications lead to the removal of p-tau from microtubules and disruption of neuronal functions. The misfold tau fragments form oligomers, and eventually aggregate as neurofibril tangle (NFT).
| MedChemExpress offers a variety of high quality peptides to meet the needs of AD pathogenesis research: | ||||||||||||||||||
|
| Reference: |
| [1] Nat Med. 2023 Sep;29(9):2187-2199. |



